
male complicationsĪn untreated infection can lead to damage and blockage of the male epididymis (the thin tube that stores sperm in the scrotum). This results in an ectopic (tubal) pregnancy in which miscarriage is unavoidable, and if rupture and bleeding occur, the mother’s life may be at risk.

If only a partial blockage occurs, the egg can still be fertilized, but may not pass from the ovary to the uterus. Infection can sometimes lead to scarring of the fallopian tubes, leading to complete blockage of the fallopian tubes and infertility. PID is characterized by pain in the pelvis and lower abdomen, as well as nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, cramps, and foul-smelling discharge. Symptoms usually appear immediately after a menstrual period, and in some cases, this is the first sign of infection. female complicationsĪmong women with untreated gonorrhea, the most common complication is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a potentially serious infection of the female reproductive tract.

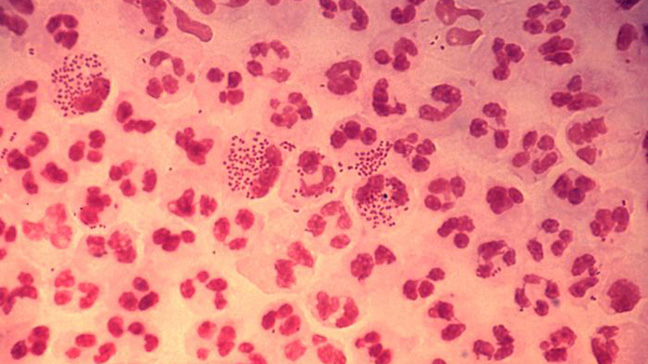
If left untreated, gonorrhea can cause serious complications that affect the reproductive tract and, less commonly, the joints, skin, heart, and central nervous system. Complications include vision loss, meningitis, septic arthritis, and blindness. In addition to conjunctivitis, other common effects include scalp infections, inflammation of the respiratory tract, vaginitis, and urethritis. This condition can usually be prevented with routine use of antibacterial eye ointment at birth for all babies.īabies usually develop symptoms within two to five days if infection cannot be avoided. When this happens, bacteria can transfer to the newborn’s eyes, causing neonatal ophthalmia, a type of conjunctivitis (eye infection) characterized by redness, pain, and discharge from the eye. Transmission can occur during childbirth when the baby comes into contact with the mother’s genital secretions. This usually doesn’t happen while the baby is in the womb. In addition to sexual transmission, vertical transmission can also occur. If signs and symptoms of gonorrhea develop, they usually appear 10 to 14 days after exposure to the virus. These symptoms can be mistaken for hemorrhoids. Rectal gonorrhea may cause mild itching, discomfort, bleeding, or pain during bowel movements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
